Science & Mathematics Education
Mathematics education cultivates students' curiosity about the world and strengthens their scientific thinking and literacy. Students achieve these learning objectives by studying Mathematics, Science, Physics, Chemistry and Biology.
| Mathematic |
A. Course objectives:
B. Course features:
|
| Combined Science |
Course objectives:
|
| Physics |
A. Course objectives
B. Course structure
|
| Chemistry |
A. Course objectives:
B. Course features
1.Diversified experiments: The chemistry class combines theory and experiments. Students carry out diversified experiments to apply the theories they have learned.
S6 students are measuring the content of vitamin C in fruit juice
2 Diversified Learning: Teachers use different learning software such as socrative, Quizzez to improve students' learning effectiveness.
3 Gifted Programs
|
| Biology |
A. Course objectives
B. Course structure
|

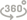


.jpg)
.jpg)